Noncurrent assets, also known as long-term assets, are resources that are not easily convertible to cash within a year. They have a longer lifespan and include items like property, plant, equipment, and investments in other companies. The accumulated depreciation account should go on the asset side of the balance sheet. Assets are ordered in terms of liquidity or how long it would take to change into cash. Current assets are the same as short-term assets and those are assets that are expected to be sold or turned into cash within one year.
What is the balance sheet formula?
That is, assets are on the left; liabilities and stockholders’ equity are on the right. When a balance sheet is prepared, the current assets are listed first and non-current assets are listed later. If you were to add up all of the resources a business owns (the assets) and subtract all of the claims from third parties (the liabilities), the residual leftover is the owners’ equity. If you’ve found that your balance sheet doesn’t balance, there’s likely a problem with some of the accounting data you’ve relied on. You may have omitted or duplicated assets, liabilities, or equity, or miscalculated your totals.
Example of a balance sheet using the report form
The insights you can gain from the balance sheet—along with other financial statements—allow you to make informed financial decisions as your business grows. These provide additional information pertaining to a company’s operations and financial position and are considered to be an integral part of the financial statements. Liabilities are obligations to parties other than owners of the business. They are grouped as current liabilities and long-term liabilities in the balance sheet.
The balance sheet equation
There are a number of high-quality accounting software solutions available. To find out which is the right option for your business, check out our article detailing the best accounting software for small businesses. When you’re starting a company, there are many important financial documents to know. It might seem overwhelming at first, but getting a handle on everything early will set you up for success in the future. Today, we’ll go over what a balance sheet is and how to master it to keep accurate financial records. Commercial paper is a form of short-term debt with a specific purpose, different from long-term debt.
Long-Term Liabilities
Assets – Fixed Assets, Current Assets, intangible assets, stock, cash, money owed from customers (accounts receivable ledger) and prepayments. The Directors Loan Account (DLA) tracks all financial transactions between a director and the company. It records any money borrowed or loaned by the director to the business, as well as any personal expenses paid for by the company on behalf of the director. It can be an asset or a liability, depending on whether the business owes or is owed the money.
With a firm understanding of the balance sheet basics, you can use this report to guide financial decision-making in your business. Although it takes time and effort to create an accurate balance sheet from scratch, it is a vital report you as a business owner should have. The two funding sources available for companies are liabilities and shareholders’ equity, which reflect how the resources were purchased. Many different financial ratios can be calculated from the information on a balance sheet. If you want to see more examples of balance sheets, look at the Companies House website. All Limited companies must submit a Balance Sheet each year, which is available to view.
They can be short-term (current liabilities) or long-term (noncurrent liabilities). A balance sheet is an important financial statement that summarizes a business’s financial situation. Balance sheets are used to evaluate a company’s performance and ability to meet its financial obligations. A report form refers to a balance sheet that presents a fiscal year in one column. The balance sheet is meant to give you a clear view of what your business owes and owns.
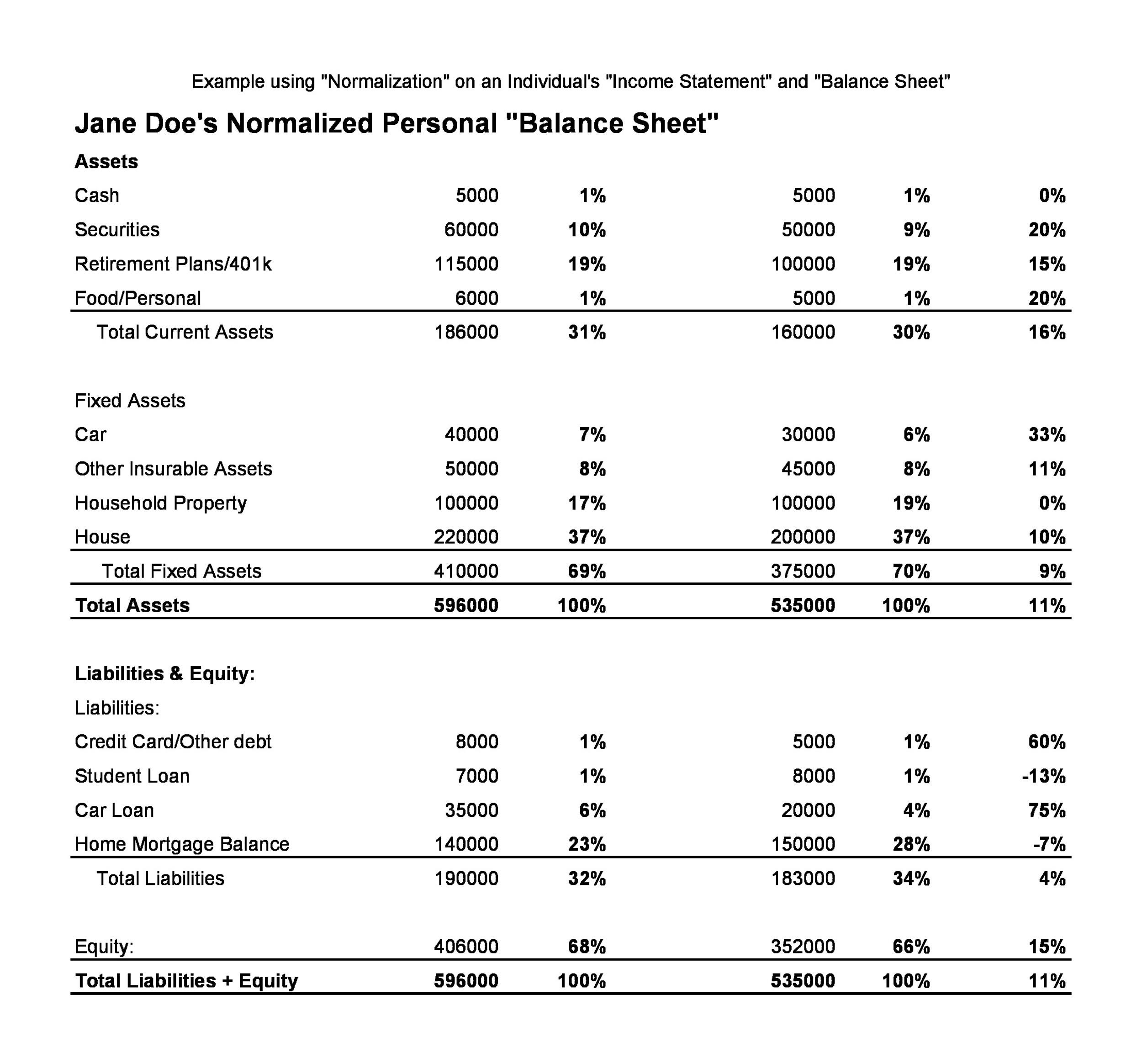
Below the assets are the liabilities and stockholders’ equity, which include current liabilities, noncurrent liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. Noncurrent or long-term liabilities are debts and other non-debt financial obligations that a company does not expect to repay within one year from the date of the balance sheet. Measuring a company’s net worth, what is an accountant and what do they do a balance sheet shows what a company owns and how these assets are financed, either through debt or equity. If necessary, her current assets could pay off her current liabilities more than three times over. Investors, business owners, and accountants can use this information to give a book value to the business, but it can be used for so much more.
- Verifying that these numbers match allows you to confirm that the data in your balance sheet is correct.
- He doesn’t have a lot of liabilities compared to his assets, and all of them are short-term liabilities.
- However, it is crucial to remember that balance sheets communicate information as of a specific date.
- Using financial ratios in analyzing a balance sheet, like the debt-to-equity ratio, can produce a good sense of the financial condition of the company and its operational efficiency.
- Similar to the accounting equation, assets are always listed first.
Assets are typically listed as individual line items and then as total assets in a balance sheet. You will need to tally up all your assets of the company on the balance sheet as of that date. This may include accounts payables, rent and utility payments, current debts or notes payables, current portion of long-term debt, and other accrued expenses.




